Brexit, denoting the United Kingdom’s separation from the European Union (EU), stands as a monumental event within contemporary political discourse. Since the pivotal referendum of 2016, Brexit has ignited fervent discussions on both national and global scales, prompting considerations regarding its perceived advantages and disadvantages. With the UK embarking on a journey independent of the EU, it becomes imperative to undertake a comprehensive and unbiased evaluation of Brexit’s merits and pitfalls.
Navigating the Pros of Brexit: Empowering Sovereignty and Economic Agility
Sovereignty and Control: Embracing Autonomy
One of the pivotal motivations behind the Brexit movement centered on the reclamation of sovereignty and the assertion of national autonomy. Proponents fervently advocated for the liberation of the United Kingdom from the perceived encroachments of European Union directives and regulations. Departing from the EU was seen as a decisive step towards restoring the nation’s ability to shape its own destiny, free from external bureaucratic influence.
Expanded Insights:
- Legal Independence: Exiting the EU offered the UK the opportunity to regain full control over its legislative framework. This meant that laws would no longer be subject to approval or alignment with EU mandates, granting British lawmakers the latitude to craft policies in accordance with domestic priorities;
- Border Management: A significant aspect of sovereignty post-Brexit was the reassumption of authority over immigration and border control. With the freedom to establish its own immigration policies, the UK could implement measures tailored to its economic and societal needs, potentially altering the demographic landscape while addressing concerns about population influx;
- Political Autonomy: Beyond legal and administrative aspects, Brexit signified a symbolic reclamation of national identity and political sovereignty. It marked a departure from the supranational governance structure of the EU, signaling the UK’s intent to chart an independent course on global affairs and diplomatic engagements.
Recommendations:
- Strategic Partnerships: Leveraging newfound sovereignty entails forging strategic partnerships and alliances beyond the EU. Cultivating robust diplomatic ties with countries sharing mutual interests can amplify the UK’s influence on the global stage while diversifying its geopolitical alliances;
- Public Engagement: Upholding sovereignty necessitates fostering public engagement and participatory governance. Encouraging citizen involvement in decision-making processes ensures that policies reflect the collective will and values of the British populace, reinforcing the legitimacy of governmental actions;
- Balancing Act: Striking a delicate balance between sovereignty and international cooperation is imperative. While asserting autonomy, maintaining constructive relations with neighboring nations and international bodies fosters collaboration on shared challenges, such as climate change and security threats.
Economic Flexibility: Navigating Trade Dynamics
Brexit proponents championed the notion of economic flexibility as a cornerstone of the UK’s post-EU trajectory. Liberated from the regulatory constraints of the European Union, the country was poised to forge bespoke trade agreements tailored to its unique economic landscape. This newfound agility promised to unlock untapped market potential, foster innovation, and fortify the nation’s economic resilience in an increasingly interconnected world.
Expanded Insights:
- Customized Trade Deals: Departing from the EU empowered the UK to negotiate trade agreements tailored to its specific interests and priorities. By eschewing the standardized approach of EU-wide trade pacts, Britain could pursue bespoke arrangements that optimize market access for its key industries, such as finance, technology, and pharmaceuticals;
- Global Market Access: Embracing economic flexibility positioned the UK to expand its trading horizons beyond the confines of the European single market. Pursuing bilateral agreements with emerging markets and established economic powerhouses unlocked a myriad of opportunities for British exporters, facilitating diversification and resilience against regional economic fluctuations;
- Innovation Ecosystem: Brexit-induced economic agility catalyzed an environment conducive to innovation and entrepreneurship. Freed from regulatory harmonization mandates, businesses were empowered to experiment with novel approaches, spur technological advancements, and capitalize on emerging market trends with nimble adaptability.
Recommendations:
- Sectoral Strategies: Crafting sector-specific trade strategies enables targeted support for industries poised to thrive in a post-Brexit landscape. Tailoring trade policies to bolster sectors of strategic importance, such as renewable energy, creative industries, and advanced manufacturing, amplifies competitive advantages and drives sustainable economic growth;
- Investment Facilitation: Streamlining investment procedures and incentivizing foreign direct investment cultivates a vibrant economic ecosystem. By fostering an investor-friendly climate characterized by regulatory clarity and financial stability, the UK can attract capital inflows, stimulate job creation, and catalyze innovation across diverse industries;
- Agility and Adaptation: Embracing a mindset of agility and adaptability is essential for navigating dynamic global trade dynamics. Continuously monitoring market trends, reassessing trade priorities, and swiftly adapting negotiation strategies empower policymakers to seize emerging opportunities and mitigate potential risks in an ever-evolving economic landscape.
Regulatory Independence Unleashed:
Embracing regulatory autonomy post-Brexit offers the UK a golden opportunity to sculpt its own legislative landscape, unbound by the constraints of EU directives. By charting its regulatory course, the nation can catalyze an environment primed for innovation, agility, and economic dynamism. Here’s how:
- Tailored Regulations: With newfound freedom, the UK can customize regulations to fit the unique requirements of its industries. This tailored approach can enhance competitiveness, stimulate growth, and address sector-specific challenges more effectively;
- Streamlined Bureaucracy: Liberated from the EU regulatory framework, the UK has the latitude to simplify bureaucratic processes, reducing red tape and fostering a more business-friendly environment. Streamlined procedures can accelerate decision-making, spur investment, and amplify entrepreneurial spirit;
- Innovation Catalyst: Independent regulation cultivates an ecosystem conducive to innovation. By facilitating experimentation and flexibility, the UK can propel groundbreaking advancements across diverse sectors, from technology and finance to healthcare and environmental sustainability;
- Global Leadership: With regulatory autonomy, the UK can position itself as a beacon of regulatory excellence on the global stage. By setting high standards, fostering transparency, and nurturing trust, the nation can attract international investment, forge strategic partnerships, and amplify its influence in shaping global regulatory norms.
Reduced Financial Obligations Unleashed:
Exiting the EU liberates the UK from the financial shackles of membership dues, empowering the nation to reallocate resources towards pressing domestic priorities. Here’s how this newfound fiscal flexibility can reshape the UK’s economic landscape:
- Domestic Investment Boost: Freed from hefty EU contributions, the UK can channel resources towards vital sectors such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Increased funding in these areas can enhance public services, improve social mobility, and fortify national resilience;
- Economic Stimulus: Redirecting funds previously earmarked for EU membership can inject a significant stimulus into the UK economy. These redirected resources can fuel job creation, bolster small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and catalyze regional development initiatives, fostering inclusive growth nationwide;
- Research and Innovation: By reinvesting in research and innovation, the UK can foster a vibrant ecosystem of scientific discovery and technological advancement. Increased funding for research institutions, startups, and R&D initiatives can propel breakthroughs, nurture talent, and reinforce the nation’s global competitiveness;
- Strategic Investments: With newfound financial autonomy, the UK can strategically deploy resources to address emerging challenges and seize opportunities. From bolstering cybersecurity infrastructure to investing in renewable energy projects, targeted investments can future-proof the nation and ensure long-term prosperity.
Challenges Arising from Brexit: Exploring the Downside

Economic Uncertainty:
In the wake of Brexit, economic uncertainty looms large, casting a shadow over various sectors and markets. The intricate process of uncoupling from the EU’s single market and customs union has ushered in a wave of apprehension, stirring concerns about the stability of trade dynamics, supply chains, and investment landscapes. Here’s a deeper look into the economic ramifications:
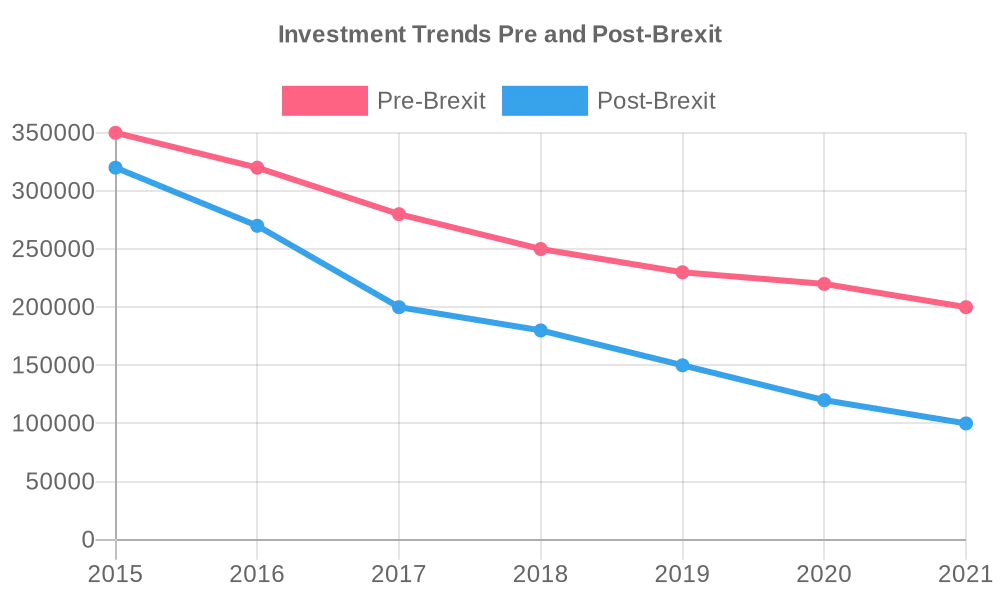
- Trade Dynamics: With the UK navigating its newfound independence from the EU, trade dynamics face unprecedented shifts. The uncertainty surrounding trade agreements and regulations poses challenges for businesses accustomed to the seamless flow of goods and services within the EU framework;
- Investment Climate: Investors, both domestic and foreign, are treading cautiously amidst the uncertainty triggered by Brexit. The ambiguity surrounding future trade policies and market conditions has prompted a reevaluation of investment strategies, with some investors adopting a wait-and-watch approach until the economic landscape stabilizes;
- Consumer Confidence: Economic uncertainty often translates into wavering consumer confidence. The uncertainty surrounding Brexit has left consumers apprehensive about their financial stability, impacting their spending behaviors and overall consumption patterns;
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The intricate web of supply chains linking the UK to the EU faces disruption as trade barriers and regulatory misalignments come into play. Businesses reliant on seamless cross-border trade are grappling with logistical complexities, delays, and increased costs associated with navigating post-Brexit trade arrangements.
Trade Disruption:
Brexit has ushered in a new era of trade relations characterized by barriers and complexities, particularly between the UK and its largest trading partner, the EU. The repercussions of this trade disruption reverberate across industries and markets, reshaping the business landscape in profound ways:
- Tariffs and Customs Checks: The imposition of tariffs and customs checks has altered the cost dynamics of trade between the UK and the EU. Businesses now face additional expenses associated with tariffs on goods crossing borders, impacting their competitiveness and profit margins;
- Regulatory Misalignment: Regulatory misalignment between the UK and the EU has compounded trade complexities, particularly for industries governed by stringent regulatory standards. Businesses operating in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food, and automotive face the arduous task of navigating divergent regulatory frameworks, potentially leading to compliance challenges and market access issues;
- Logistical Challenges: The introduction of trade barriers has exacerbated logistical challenges for businesses engaged in cross-border trade. Delays at border crossings, increased paperwork, and administrative burdens have become commonplace, disrupting supply chains and impeding the timely delivery of goods;
- Impact on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs, often lacking the resources and infrastructure of larger corporations, are particularly vulnerable to the trade disruptions triggered by Brexit. The increased trade costs and administrative burdens place strain on the operational capabilities of SMEs, potentially hindering their ability to compete in the international market.
Diminished Global Influence:
Before Brexit, the United Kingdom (UK) held a significant position on the world stage through its membership in the European Union (EU). The collective diplomatic and economic strength of the EU bolstered the UK’s influence, allowing it to participate in shaping global events and policies. However, with Brexit, the UK’s global influence has undergone a noticeable reduction. Here’s how:
- Weakened Presence in International Negotiations: Exiting the EU has weakened the UK’s position in international negotiations. Without the backing of the EU bloc, the UK now lacks the collective bargaining power it once enjoyed, making it more challenging to assert its interests on issues ranging from trade agreements to climate change initiatives;
- Limited Role in EU Institutions: As a former member state, the UK no longer has direct representation within EU institutions such as the European Parliament and the European Commission. This absence diminishes its ability to directly influence EU policies and decisions that may still impact its interests, such as trade regulations and market access;
- Reevaluation of Diplomatic Relationships: Brexit has prompted the UK to reevaluate its diplomatic relationships and alliances. With its traditional ties to EU member states shifting, the UK must forge new partnerships and strengthen existing ones to maintain its relevance on the global stage. This may involve deepening ties with non-EU countries, pursuing closer cooperation with international organizations like the United Nations, or enhancing transatlantic relations with the United States.
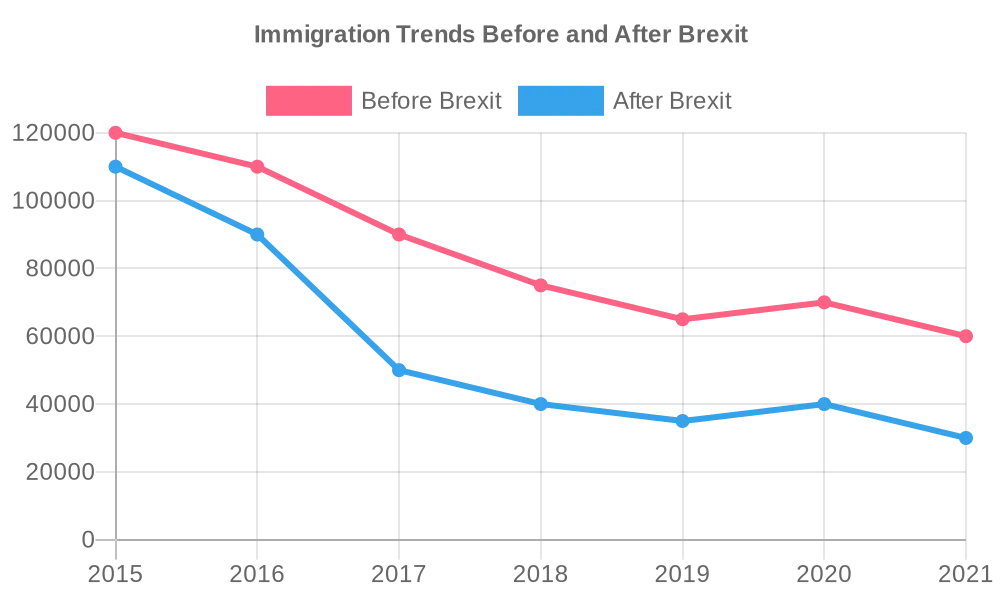
Impact on Immigration and Labor Dynamics:
Brexit’s ramifications extend beyond geopolitical considerations to directly impact immigration policies and labor dynamics within the UK. While Brexit affords the UK greater autonomy over its borders, it also introduces complexities and uncertainties regarding immigration and the labor market. Here’s a closer look at the impact:
- Control Over Immigration Policies: Exiting the EU grants the UK control over its immigration policies, allowing it to implement stricter border controls and tailor migration regulations to its specific needs and priorities. This newfound autonomy enables the UK to prioritize skilled migration, address concerns about uncontrolled immigration, and respond to domestic political pressures;
- Disruption to Labor Supply: Brexit has raised concerns about potential disruptions to the flow of labor from EU countries. Many industries in the UK, such as agriculture, healthcare, and hospitality, rely heavily on migrant workers from the EU to fill labor gaps. Restrictions on freedom of movement post-Brexit could exacerbate existing skills shortages in these sectors, leading to labor market imbalances and impacting productivity;
- Shift in Workforce Dynamics: The changes brought about by Brexit are likely to reshape the composition of the UK workforce. Employers may need to adapt their recruitment strategies, invest in training programs to upskill domestic workers, or explore alternative sources of labor to mitigate the effects of reduced EU migration. Additionally, Brexit could influence wage dynamics and employment conditions as employers adjust to the new regulatory landscape.
Conclusion
The ongoing discourse regarding Brexit continues to spark heated debate, as advocates and detractors present contrasting perspectives on its potential ramifications. While Brexit presents prospects for heightened sovereignty, enhanced economic adaptability, and greater regulatory independence, it simultaneously presents obstacles such as economic instability, trade disturbances, reduced global sway, and immigration issues. As the United Kingdom charts its course in the aftermath of Brexit, decision-makers are tasked with diligently assessing these advantages and disadvantages to mitigate potential hazards and leverage opportunities for the nation’s enduring welfare and equilibrium.