Following the United Kingdom’s momentous choice to depart from the European Union, colloquially known as Brexit, there has ensued a flurry of speculation and apprehension regarding its ramifications across diverse economic domains. Among these, the housing market stands out prominently. Given the prevailing uncertainties surrounding trade pacts, immigration regulations, and overall economic equilibrium, a pervasive curiosity has arisen regarding the potential effects of Brexit on residential property prices throughout the UK.
Pre-Brexit Expectations Unveiled:
Before the historic Brexit referendum shook the UK’s political landscape in June 2016, speculation loomed large over the fate of the housing market. Anticipation was rife that severing ties with the European Union might cast a shadow of uncertainty, potentially triggering a downturn in the property sector. These apprehensions stemmed from a variety of factors, chiefly economic instability, concerns over diminished foreign investments, and a potential dent in consumer confidence. Analysts and industry experts braced for impact, contemplating the possible ramifications of such a monumental decision.
In the pre-Brexit landscape, stakeholders across the housing market spectrum braced themselves for what could be a seismic shift in dynamics. Here’s an in-depth look at the pre-Brexit expectations:
Factors Fueling Pre-Brexit Concerns:
- Economic Instability: The looming prospect of Brexit stirred fears of economic instability, prompting speculation about its potential ripple effects on the housing market;
- Diminished Foreign Investment: The UK’s departure from the EU raised concerns about dwindling foreign investments, which had been crucial drivers of growth in the property sector;
- Decreased Consumer Confidence: Uncertainty surrounding Brexit clouded consumer sentiment, potentially dampening enthusiasm for property purchases and sales.
Mitigating Pre-Brexit Risks:
- Diversification Strategies: Property investors explored diversification strategies to mitigate risks associated with Brexit-related uncertainties, considering alternative investment avenues beyond traditional residential real estate;
- Flexible Financing Options: Buyers and sellers alike sought flexible financing options to navigate potential fluctuations in property prices and mortgage rates, ensuring resilience in the face of market volatility;
- Market Monitoring and Analysis: Industry stakeholders intensified efforts to monitor and analyze market trends, leveraging data-driven insights to anticipate and adapt to changing conditions effectively.
Post-Brexit Realities Unveiled:
In the wake of the Brexit referendum, the housing market embarked on a rollercoaster ride, navigating through a landscape characterized by uncertainty and flux. As the dust settled on the historic decision, post-Brexit realities began to take shape, unveiling a complex interplay of factors shaping the market dynamics.
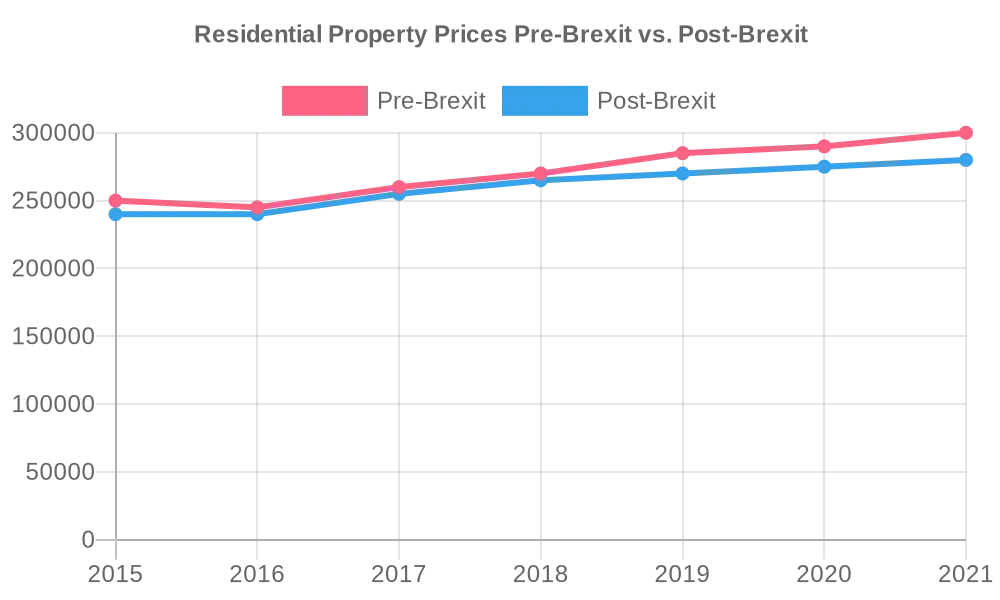
Post-Brexit Realities Explored:
- Initial Market Slowdown: In the immediate aftermath of the Brexit referendum, ambiguity surrounding the terms of the UK’s departure from the EU cast a shadow of uncertainty over the housing market. Both buyers and sellers adopted a cautious stance, leading to a temporary slowdown in activity as they awaited clarity on the future trajectory;
- Negotiation Progress and Confidence Restoration: As Brexit negotiations progressed and a clearer picture emerged regarding the UK’s post-Brexit arrangements, confidence gradually returned to the housing market. Clarity on trade deals, immigration policies, and regulatory frameworks helped alleviate uncertainties, fostering a resurgence in buyer and seller confidence;
- Regional Disparities and Resilience: Despite the overarching impact of Brexit on the housing market, regional disparities emerged, with some areas exhibiting greater resilience than others. Factors such as local economic dynamics, employment trends, and housing supply-demand dynamics played a pivotal role in shaping regional variations in market performance.
Navigating Post-Brexit Realities:
- Stay Informed: Stay abreast of Brexit-related developments, including trade agreements, regulatory changes, and economic indicators, to gauge their potential impact on the housing market;
- Adaptability is Key: Remain flexible and adaptable in response to evolving market conditions, adjusting strategies and approaches as needed to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate risks;
- Diversify Investments: Consider diversifying property investments across regions and asset classes to spread risk and capitalize on varied market dynamics;
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with real estate professionals, financial advisors, and legal experts to gain insights and guidance tailored to your specific circumstances, ensuring informed decision-making in navigating post-Brexit realities.
Regional Disparities:
The impact of Brexit on the UK’s housing market has been a tale of contrasting fortunes, with regional disparities highlighting the nuanced effects across the country. While London, as a global financial powerhouse, initially weathered uncertainty as businesses contemplated relocations and foreign investors reassessed their positions, the market has since found its footing. However, the pace of growth in the capital has tempered compared to its pre-Brexit vigor.
Meanwhile, regions beyond the confines of London and the affluent South East have experienced a more diverse range of outcomes. Some areas have witnessed substantial upticks in property values, propelled by a confluence of factors, including heightened demand for suburban and rural dwellings. Here’s a closer look at how Brexit, coupled with other economic dynamics, has influenced housing trends across various regions:
- London and the South East:
- Initially faced turbulence as businesses and investors navigated uncertainty;
- Market has stabilized, albeit with more subdued growth compared to pre-Brexit years;
- Affluent areas may still see robust demand, albeit tempered compared to the past;
- High-value properties continue to attract interest from domestic and international buyers.
- Northern Regions:
- Witnessing varied outcomes, with some areas experiencing significant increases in property values;
- Factors driving growth include increased demand for suburban and rural living spaces;
- Relatively lower property prices compared to London make these regions attractive to buyers seeking affordability.
- Midlands and Central England:
- Mixed performance, with urban centers experiencing moderate growth while rural areas see increased interest;
- Infrastructure improvements and government investment in certain areas may drive future growth;
- Emerging tech and business hubs may attract property investment, bolstering local housing markets.
- Devolved Nations (Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland):
- Economic factors intertwined with Brexit impact vary across these regions;
- Local government policies and economic diversification efforts influence housing market resilience;
- Some areas may benefit from increased autonomy in shaping policies post-Brexit.
By understanding these regional nuances, buyers, sellers, and investors can make more informed decisions tailored to specific market conditions and opportunities.
Economic Factors:
Brexit’s ripple effects extend beyond regional disparities, intersecting with a myriad of economic factors that collectively shape the housing landscape. Amidst the uncertainty, several key drivers have emerged, influencing market dynamics across the UK:
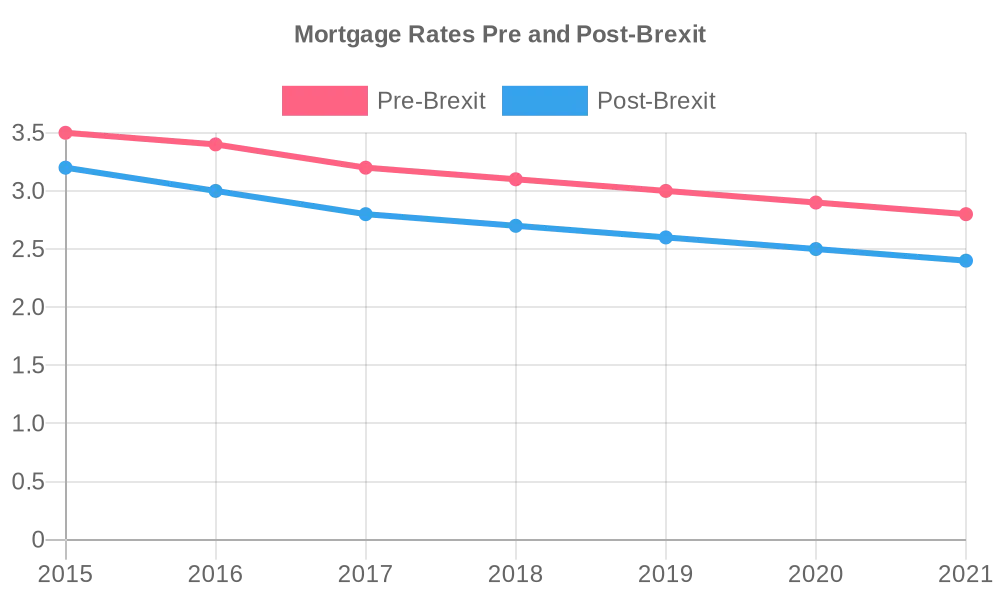
- Historically Low-Interest Rates:
- Continuation of historically low-interest rates has bolstered affordability and incentivized borrowing;
- Lower mortgage rates make homeownership more accessible, potentially stimulating demand.
- Government Schemes like Help to Buy:
- Initiatives such as Help to Buy have provided crucial support to first-time buyers, stimulating demand in certain segments;
- While these schemes have contributed to homeownership rates, they also face scrutiny for potentially inflating property prices.
- COVID-19 Pandemic Impact:
- Changes in consumer behavior due to the pandemic have reshaped housing preferences;
- Increased focus on remote work has fueled demand for properties with dedicated home office spaces and outdoor amenities;
- Suburban and rural areas have seen heightened interest as individuals seek larger living spaces and access to nature.
- Shifts in Working Patterns:
- Remote work trends have accelerated, leading to increased flexibility in location choices for homebuyers;
- Proximity to urban centers is no longer the primary driver for property decisions, with lifestyle factors gaining prominence;
- Commute times and access to amenities are re-evaluated as individuals prioritize work-life balance.
- Consumer Sentiment and Confidence:
- Uncertainty surrounding Brexit negotiations and economic outlooks have influenced consumer sentiment;
- Confidence in the housing market fluctuates in response to geopolitical events and economic indicators;
- Perception of market stability and future prospects shapes buyer behavior and investment decisions.
Future Outlook
As the United Kingdom transitions into a new era post-Brexit, the landscape of its housing market undergoes a dynamic transformation, influenced by a multitude of factors. While the aftermath of Brexit still casts a shadow of uncertainty, particularly concerning trade agreements and immigration regulations, economists uphold a tempered optimism regarding the trajectory of the housing market in the long run. Here’s a comprehensive look at the various elements shaping the future outlook of the UK housing market:

- Housing Shortage Continues:
- Despite fluctuations in demand and supply, the underlying issue of housing shortage persists in the UK;
- Rapid urbanization, population growth, and changing demographics contribute to the ongoing imbalance between housing supply and demand;
- This shortage not only fuels competition among buyers but also exerts upward pressure on housing prices, particularly in high-demand areas.
- Government Initiatives to Foster Homeownership:
- The government continues to introduce policies and initiatives aimed at stimulating homeownership and addressing affordability concerns;
- Schemes such as Help to Buy, Shared Ownership, and First Homes aim to assist first-time buyers and low-income households in entering the property market;
- Additionally, incentives for property developers to build affordable housing and initiatives to revitalize urban areas contribute to the overall housing market dynamics.
- Impact of Trade Relationships and Immigration Policies:
- The UK’s trade relationships post-Brexit, along with immigration policies, have significant ramifications for the housing market;
- Trade agreements influence economic stability, employment rates, and consumer confidence, all of which directly impact the housing sector;
- Immigration policies affect population dynamics, influencing both demand for housing and the composition of the workforce, particularly in sectors reliant on migrant labor.
- Pent-up Demand and Market Resilience:
- Despite short-term fluctuations and uncertainties, pent-up demand remains a driving force in the housing market;
- Factors such as delayed purchases due to economic uncertainty, lifestyle changes prompted by the pandemic, and the desire for larger living spaces contribute to pent-up demand;
- The resilience of the housing market, demonstrated by its ability to adapt to changing circumstances and maintain stable growth over time, instills confidence among investors and stakeholders.
- Technological Advancements and Adaptation:
- Technological innovations continue to shape the real estate industry, influencing various aspects from property searches to transaction processes;
- Virtual property viewings, blockchain-based transactions, and AI-driven market analysis tools are revolutionizing how buyers, sellers, and agents engage in the housing market;
- Embracing these advancements not only enhances efficiency and transparency but also opens up new avenues for investment and market participation.
Conclusion
The effects of Brexit on the housing landscape in the UK have been multifaceted, showing a nuanced pattern of influence that differs from region to region. Although the anticipated drastic decline failed to manifest initially, the market grappled with a series of obstacles and uncertainties in its wake. As the nation undergoes the process of adjusting to its revised association with the EU amidst broader economic and societal transformations, the housing sector remains a mirror reflecting these dynamic changes. Amidst the hurdles, there exist grounds for tentative optimism regarding the enduring strength of the UK’s real estate domain over the extended period.